Electrocardiogram
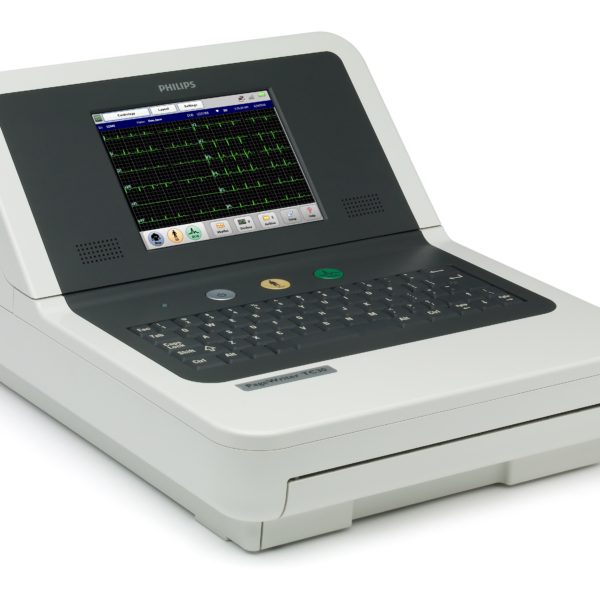
The PageWriter TC20 is advanced, easy to use, and affordable while still supporting your evolving workfl ow needs. The 1-2-3 touch operation leads you through acquisition, analysis, storage, printing, and accessing previous ECGs with ease. Further enhancing efficiency, worklists and patient demographics can be downloaded using wired or wireless LAN via standard XML, HL7, and DICOM communications. PageWriter’s native DICOM interoperability provides direct access to ECG orders from your current DICOM MWL provider and storage of resulting DICOM format ECGs to your existing PACS. The TC20 also provides the world class DXL Algorithm with industry leading clinical decision support.
Courtesy: Philips
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart’s electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction, and electrolyte disturbances.)
In a 12-lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient’s limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart’s electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (“leads”) and is recorded over a period of time (usually ten seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart’s electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle.
There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave, which represents repolarization of the ventricles
Source: Wikipedia

