X-radiation
X-ray (or much less commonly, X-radiation) is a high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light. Unlike light, however, x-rays have higher energy and can pass through most objects, including the body. Medical x-rays are used to generate images of tissues and structures inside the body. If x-rays traveling through the body also pass through an x-ray detector on the other side of the patient, an image will be formed that represents the “shadows” formed by the objects inside of the body.
One type of x-ray detector is photographic film, but there are many other types of detectors that are used to produce digital images. The x-ray images that result from this process are called radiographs.
To create a radiograph, a patient is positioned so that the part of the body being imaged is located between an x-ray source and an x-ray detector. When the machine is turned on, x-rays travel through the body and are absorbed in different amounts by different tissues, depending on the radiological density of the tissues they pass through. Radiological density is determined by both the density and the atomic number (the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus) of the material being imaged. For example, our bones contain calcium, which has a higher atomic number than most other tissues. Because of this property, bones readily absorb x-rays and therefore produce high contrast on the x-ray detector. As a result, bony structures appear whiter than other tissues against the black background of a radiograph. Conversely, x-rays travel more easily through less radiologically dense tissues, such as fat, muscle, and air-filled cavities such as the lungs. These structures are displayed in shades of gray on a radiograph.
Diagnostic
X-ray radiography: Detects
bone fractures, certain tumors and other abnormal masses, pneumonia, some types of injuries, calcifications, foreign objects, or dental problems.
Source: U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
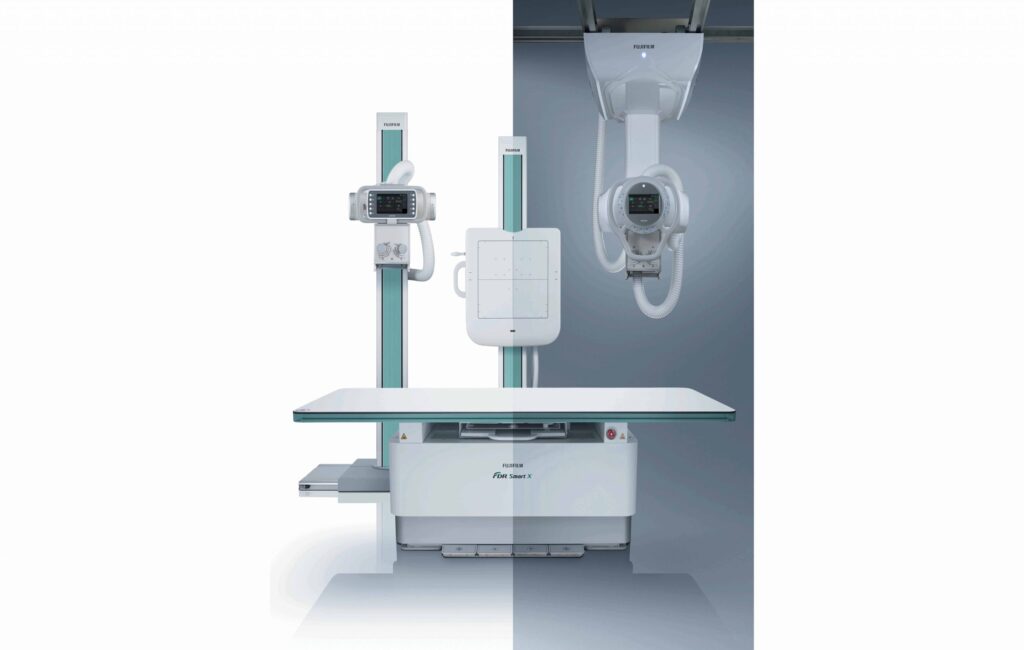
Fujifilm FDR Smart X
Wall Bucky Stand Automatic Tilting
Automatic and manual tilting of the upright bucky stand is available. Providing an improved workflow for the radiographers and an improved experience to those patients in wheelchairs.
Removable Grid
Removable grids in both the table and upright stand, allow flexible working (such as Pediatrics).
Dual Reference Rotation
Not only top reference, but also center rotation can be selected when using 14″ x 17″DR panels. This provides flexible solutions, enabling exposure of areas other than the chest without taking out the panel and insert again in rotated direction or using larger panel.
Automatic Tracking
Tube head and bucky move synchronized with each other supporting positioning for exposure.
Elevating Patient Table
A
motorized height adjustable floating top table with a weight limit of 300 kg. Synchronisation (Tracking) of the tube with both upright and table detectors. Available with ceiling and floor mounted systems.
Rotating Tray
Rotating tray is also available for table. Direction of the panel can be changed according to the patient position.

